What is syphilis?
Syphilis is an STD that can cause long-term complications and/or death if not treated correctly. Symptoms in adults are divided into stages. These stages are primary, secondary, latent, and late syphilis.
How is syphilis spread?
You can get syphilis by direct contact with a syphilis sore during anal, vaginal, or oral sex. Sores can be found on the penis, vagina, anus, in the rectum, or on the lips and in the mouth. Syphilis can also be spread from
an infected mother to her unborn baby.
What does syphilis look like?
Syphilis has been called ‘the great imitator’ because it has so many possible symptoms, many of which look like symptoms from other diseases. The painless syphilis sore that you would get after you are first infected can be confused for an ingrown hair, zipper cut, or other seemingly harmless bump. The non-itchy body rash that develops during the second stage of syphilis can show up on the palms of your hands and soles of your feet, all over your body, or in just a few places. You could also be infected with syphilis and have very mild symptoms or none at all.
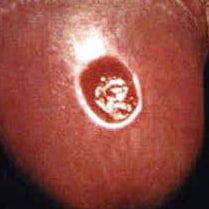
Example of a primary syphilis sore.
How can I avoid getting syphilis?
You can protect yourself from getting syphilis by:
- Not having sex;
- Being in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and has negative STD test results; and
- Using latex condoms and dental dams the right way every time you have sex.
Washing your genitals, urinating, or douching after sex will notprotect you from getting syphilis.
Am I at risk for syphilis?
Any sexually active person can get syphilis through unprotected anal, vaginal, or oral sex. Have an honest and open talk with your health care provider and ask whether you should be tested for syphilis or other STDs. You should get tested regularly for syphilis if you are pregnant, are a
man who has sex with men, have HIV infection, and/or have partner(s) who have tested positive for syphilis.
I’m pregnant. How does syphilis affect my baby?
If you are
pregnant and have syphilis, you can give the infection to your unborn baby. Having syphilis can lead to a low birth weight baby. It can also make it more likely you will deliver your baby too early or stillborn (a baby born dead). To protect your baby,
you should be tested for syphilis during your pregnancy and at delivery and receive immediate treatment if you test positive.
An infected baby may be born without signs or symptoms of disease. However, if not treated immediately, the baby may develop serious problems within a few weeks. Untreated babies can have health problems such as cataracts, deafness, or seizures, and can die.
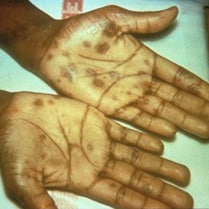
Secondary rash from syphilis on palms of hands.
How do I know if I have syphilis?
Symptoms of syphilis in adults can be divided into stages:
Primary Stage
During the first (primary) stage of syphilis, you may notice a single sore, but there may be multiple sores. The sore is the location where syphilis entered your body. The sore is usually firm, round, and painless. Because the sore is painless, it can easily go unnoticed. The sore lasts 3 to 6 weeks and heals regardless of whether or not you receive treatment. Even though the sore goes away, you must still receive treatment so your infection does not move to the secondary stage.
Secondary Stage
During the secondary stage, you may have skin rashes and/or sores in your mouth, vagina, or anus (also called mucous membrane lesions). This stage usually starts with a rash on one or more areas of your body. The rash can show up when your primary sore is healing or several weeks after the sore has healed. The rash can look like rough, red, or reddish brown spots on the palms of your hands and/or the bottoms of your feet. The rash usually won’t itch and it is sometimes so faint that you won’t notice it. Other symptoms you may have can include fever, swollen lymph glands, sore throat, patchy hair loss, headaches, weight loss, muscle aches, and fatigue (feeling very tired). The symptoms from this stage will go away whether or not you receive treatment. Without the right treatment, your infection will move to the latent and possibly late stages of syphilis.
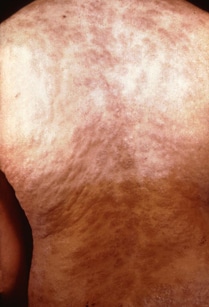
Secondary rash from syphilis on torso.
Latent and Late Stages
The latent stage of syphilis begins when all of the symptoms you had earlier disappear. If you do not receive treatment, you can continue to have syphilis in your body for years without any signs or symptoms. Most people with untreated syphilis do not develop late stage syphilis. However, when it does happen it is very serious and would occur 10–30 years after your infection began. Symptoms of the late stage of syphilis include difficulty coordinating your muscle movements, paralysis (not able to move certain parts of your body), numbness, blindness, and dementia (mental disorder). In the late stages of syphilis, the disease damages your internal organs and can result in death.
A syphilis infection is called an
‘early’ case if a patient has been infected for a year or less, such as during the primary or secondary stages of syphilis. People who have ‘early’ syphilis infections can more easily spread the infection to their sex partners. The majority of early syphilis cases are currently found among
men who have sex with men, but women and unborn children are also at risk of infection.
How will my doctor know if I have syphilis?
Most of the time, a blood test can be used to test for syphilis. Some health care providers will diagnose syphilis by testing fluid from a syphilis sore.
Can syphilis be cured?

Darkfield micrograph ofTreponema pallidum.
Yes, syphilis can be cured with the right antibiotics from your health care provider. However, treatment will not undo any damage that the infection has already done.
I’ve been treated. Can I get syphilis again?
Having syphilis once does not protect you from getting it again. Even after you’ve been successfully treated, you can still be re-infected. Only laboratory tests can confirm whether you have syphilis. Follow-up testing by your health care provider is recommended to make sure that your treatment was successful.
Because syphilis sores can be hidden in the vagina, anus, under the foreskin of the penis, or in the mouth, it may not be obvious that a sex partner has syphilis. Unless you know that your sex partner(s) has been tested and treated, you may be at risk of getting syphilis again from an untreated sex partner.











































.jpg)






